
1. Introduction
Although cold chain logistics has been around for several decades, it is not considered “conventional.” Traditional logistics typically involves moving goods that do not require specific temperature controls, focusing on efficiency, speed, and effectiveness. Cold chain logistics, however, differs in several key ways, primarily due to the need to maintain specific temperature conditions throughout the supply chain. This includes temperature control, infrastructure, technology and monitoring, regulatory requirements, cost, and risk management.
This blog will provide a comprehensive overview of cold chain logistics compared to conventional logistics.
2. What is Cold Chain Logistics?
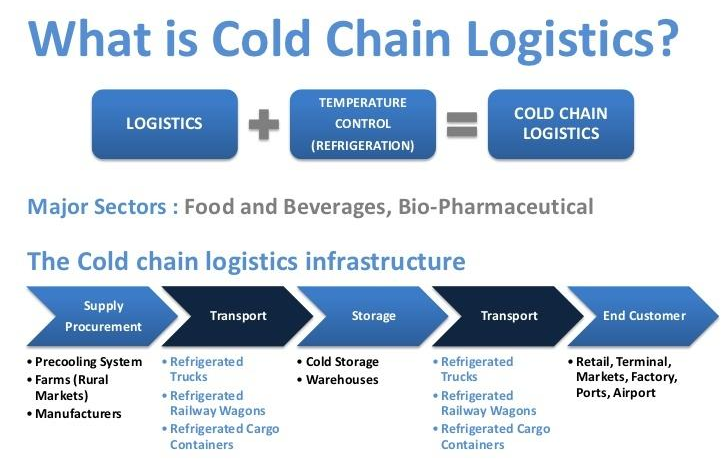
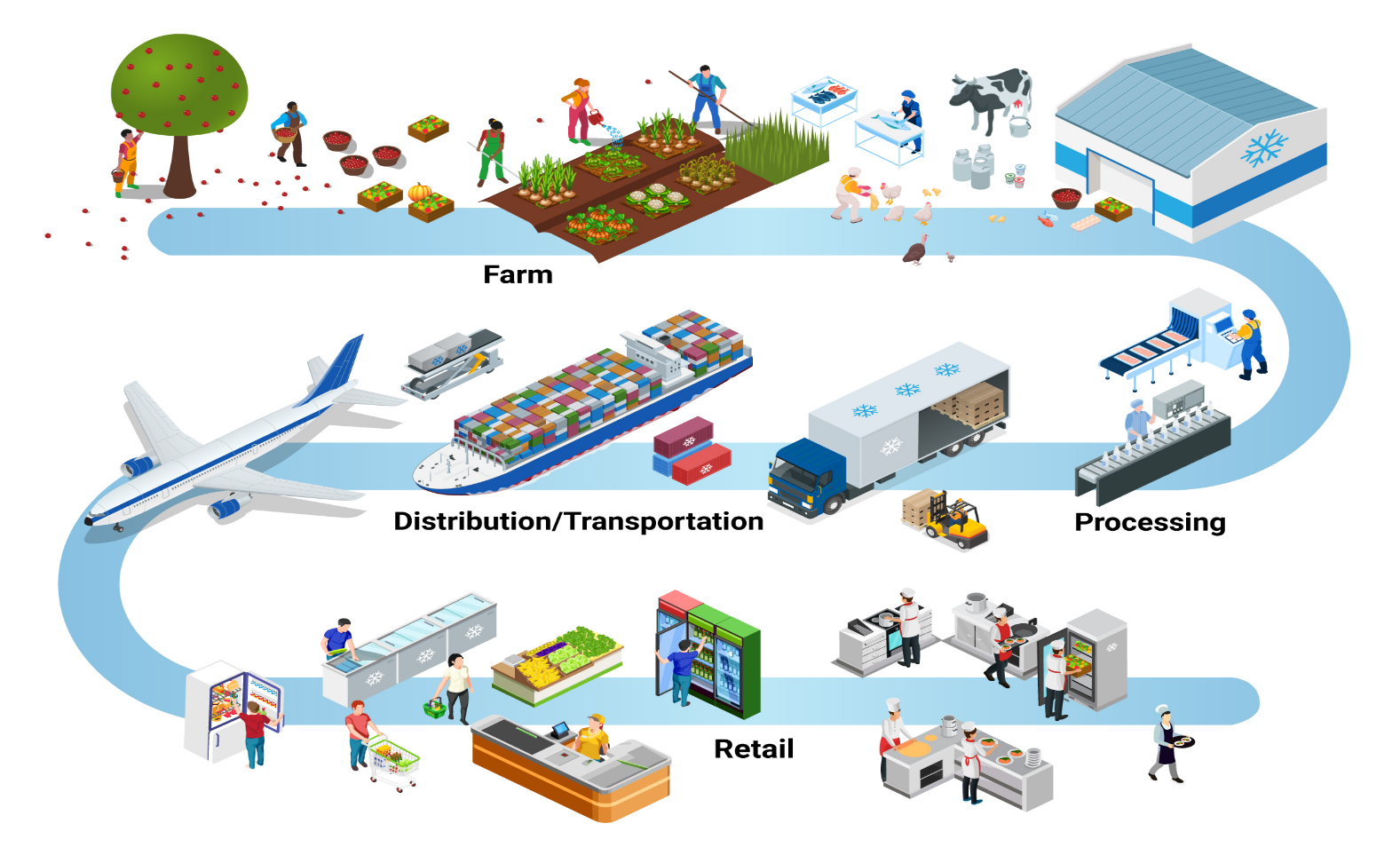
Cold chain logistics refers to the handling, storing, and transporting of temperature-sensitive goods—such as pharmaceuticals, food products, and chemicals—through a carefully temperature-controlled supply chain. This ensures products remain within a specific temperature range from origin to destination.
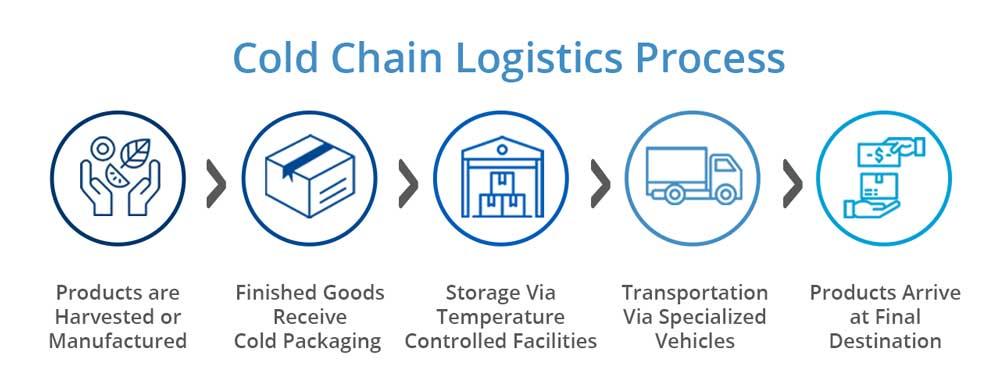

Storage typically involves using special facilities (cold storage) to keep products within a specific temperature range. These include refrigerated warehouses and cold rooms.
- Refrigerated warehouses are large facilities equipped with refrigeration systems to maintain the desired product temperatures.
- Cold rooms are smaller, temperature-controlled spaces used for storing perishable products. Larger cold storage facilities generally house multiple cold rooms for smaller-scale use.
3.1. Cold Transport
Cold transport refers to moving temperature-sensitive goods from one place to another while keeping the products at the desired temperature. This is done using refrigerated trucks, ships, and airplanes.
- Refrigerated trucks and containers use built-in refrigeration units,
sometimes using liquid nitrogen, to maintain constant temperatures
for long-distance transport. - Refrigerated ships have large, refrigerated cargo holds for sea
transport. - Airplanes with temperature-controlled cargo holds ensure quick
transport over long distances.

Cold chain logistics encompasses many elements in packaging that help keep temperature-sensitive products safe and effective.
3.2. Packaging
Packaging plays a vital role in protecting temperature- sensitive goods from fluctuations. Industries use various technologies and materials, such as insulated boxes, gel packs, and dry ice, to keep products at the right temperature. Advanced technologies like vacuum insulation panels and phase change materials help maintain stable temperatures during storage and transit.
3.3. Temperature Monitoring in Storage and Transit
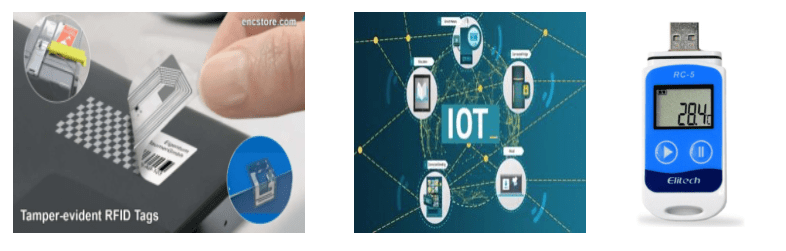
Temperature monitoring technologies, such as RFID tags and IoT sensors, are critical in tracking the temperature, humidity, and condition of products in real-time throughout the supply chain. This data allows for immediate corrective action if problems arise, ensuring products remain safe and of high quality.
Constant temperature monitoring is paramount in cold logistics.
3.4. Compliance with Regulations
Regulatory compliance is crucial in cold chain logistics, helping maintain product quality, prevent spoilage, and ensure customer safety.
Storage & Transport Temperature Ranges for Various Products:
- Fruits: 0°C to 5°C – slows down ripening, prevents spoilage, and
keeps fruits fresh. - Dairy products: 1°C to 3°C
- Pharmaceuticals: 2°C to 8°C – necessary for maintaining the potency and effectiveness of medicines and vaccines.
- Frozen food: Below -18°C – prevents bacterial growth and thawing.
- Seafood: 0°C – prevents spoilage and maintains quality.
Organizations such as the WHO (World Health Organization) and the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) set standards for the proper handling and storage of food, medicines, and vaccines to ensure safety and quality.
Conclusion
Cold chain logistics reduces product loss by maintaining the desired temperature throughout the supply chain, extending shelf life, and enhancing public safety.

